|
|
Natural Gas |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 June 2014 02:56 PM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Natural gas is fast growing energy in the recent times owing to its relatively clean combustion and fuel efficiency. Similar to the other non-renewable energies like crude and coal, it is also a fossil fuel and found in deep underground rock formations. It is usually found in close proximity to coal deposits and /or to petroleum reserves. Natural gas is a mixture of hydrocarbon gas mainly consisting of methane along with other atmospheric gases in minor quantities. It is a colourless and odourless in its pure form.
Natural gas is measured in British Thermal Units (Btu) for pricing. One Btu is the amount of natural gas that will produce enough energy to heat one pound of water by one degree at normal pressure. Nevertheless, production and distribution of natural gas is commonly measured in cubic feet.
Natural gas was first reported to have identified as a source of fuel on commercial scale in China as early as in 500 BC transferring it through bamboo pipeline. First commercial production of natural gas was reported to have started in 1820s in Fredonia, New York by William Hart.
Important Uses:
Natural gas is an important source of fuel energy with relatively less toxic emissions than any other fossil fuels.
It is widely used in electricity generation, as industrial feedstock, for lighting, cooking and transportation. It is gaining popularity as an alternative source of automobile fuel in its compressed form.
Production process: Production of natural gas involves three steps
1. Exploration and identification of gas deposit locations.
2. Extraction involves drilling a well and extraction of gas from the underground to the surface through the well.
3. Processing for separation of various by-products like sulphur, ethane, propane, butane etc.,
World Scenario
World’s natural gas reserves stood at about 6844 trillion cubic feet (mcf) as at the end of 2012. Natural gas production in the world has risen to 120 trillion cubic feet in 2012 from about 88.8 mcf in 2001 registering an average annual growth rate of about 3%.
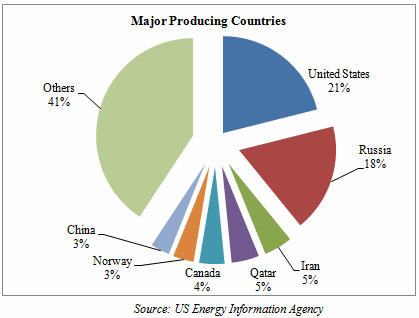 The major producing countries are U.S., Russia, Iran, Qatar and Canada. US is the single largest producer accounting for about 21% of world production followed by Russia with about 18% share, Iran with 4.7%, Qatar with 4.6% and Canada with about 4.2% of share in total natural gas production in the world.
Table 1: World natural gas production, consumption and trade (bcf)
Source: US EIA
Consumption of natural gas by major countries indicated a similar pattern with the U. S. playing a dominant role contributing for about 21% of total world’s consumption followed by Russia with about 13%, Iran with 4.6%, china with 4.3% and Japan with 3.8% share.
On the other hand, trade in natural gas has remained largely stable from mid-2000s at around 35 trillion cubic feet. Major exporting countries of natural gas are Russia with 20%, Qatar with 12%, Norway with 11% and Canada with 8.5% share in the total exports of natural gas in the world. Qatar has emerged as a second largest exporter since 2010 onwards posting a rapid growth from mid-2000s while the exports from others remained largely stable.
Japan is the largest importer of natural gas accounting for 11% of total imports followed by U.S. with about 8.5% and Germany with about 8.3% share. Imports by the U.S. declined significantly from mid-2000s owing to the rise in production, whereas imports by Japan and U.K. rose steadily and significantly throughout the 2000s.
Domestic Scenario
It is estimated that India has about 1354 billion cubic meters of natural gas reserves available in the country as at the end of 2013. Majority of the reserves are located in western and eastern offshore, while the rest are distributed in the onshore area of Gujarat, Assam, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
Major producers of natural gas in India are Oil & Natural Gas Corporation Ltd. (ONGC), Oil India Limited (OIL) and JVs of Tapti, Panna-Mukta and Ravva. Major marketing agency of gas in India is the Gas Authority of India Ltd (GAIL).
Table 2: Domestic natural gas production, consumption and trade (bcf)
Source: US EIA
Natural gas production in India has increased significantly during the late 2000s but moderated in 2011 and 2012. Nevertheless, consumption continued to progress at a steady pace during the past decade. As a result, imports have also been increasing steadily and reached nearly 600 bcf in 2012.
In line with the distribution of reserves, production of natural gas largely comes from offshore areas to an extent of about 70-80%. Within the offshore areas, western offshore of Gujarat contributes for more than 60% of offshore production and more than 50% of total production.
Onshore production mainly comes from Assam, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. Marginal quantities are also produced from states like Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Rajasthan and West Bengal.
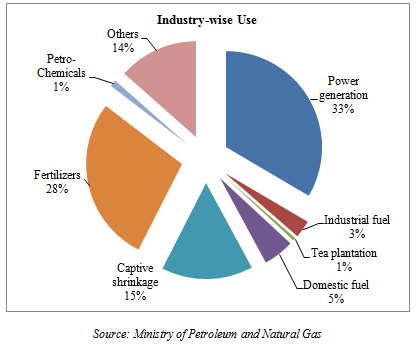 Industry-wise use of natural gas suggested that nearly 1/3rd of gas consumption is for power generation followed by fertilizer industry, captive shrinkage and domestic fuel purposes. Natural gas is also used for other purposes like industrial fuel, petro-chemicals and tea plantations.
Major Markets
Spot markets: Mumbai, Delhi
Futures markets:
International: Nymex
Domestic: MCX
External Trade
India is a net importer of natural gas to an extent of 500-600 trillion cubic feet per year. Imports account for about 25% of domestic consumption. Imports have been rising steadily with the rising demand. India doesn’t export natural gas.
Major export destinations: NA
Major import sources: Qatar, Oman, Malaysia and to some extent Egypt and Australia.
Factors Influencing Prices
· Unlike in other commodities natural gas prices are still controlled by ministry of petroleum and natural gas through the administered price mechanism (APM).
· Natural gas prices were fixed by ONGC/OIL before 1987 but with effect from 30.1.1987 the prices are fixed by the Government through APM.
· About 80% gas is priced under APM and the rest is through long-term bilateral contracts. Thus, spot prices are not influenced by day-to-day events and are relatively stable.
· However, natural gas futures prices offered on MCX are tracking and settled at Nymex futures prices but not the domestic natural gas market. Thus, in order to track natural gas futures on MCX it is necessary to follow the natural gas market in U.S.
|
Copyright © CC Commodity Info Services LLP. All rights reserved.

