|
|
Guar |
| 03 March 2015 04:02 PM |
 |
|
Cluster bean or commonly known as Guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.) is a drought-tolerant legume. It was traditionally cultivated for using as a vegetable and fodder. Commercial interest for Guar is fairly recent and its large-scale industrial production started from the 1950s. The origin of guar is very well known but historical evidence suggests that it must have been domesticated from African species of Cymopsis. Traditionally, guar seed has been cultivated in India and Pakistan.
Commercial cultivation of guar seed is primarily triggered by the demand for guar gum production. Major world suppliers of guar gum are India, Pakistan and the United States, with smaller contribution from Australia and Africa.
Economically Important Product:
Guar is commercially cultivated for its seed which contains uniquely large endosperm.
Guar gum is the main product of endosperm and contains galactomannan, which forms a viscous gel in cold water. Gum recovery is about 29% of seed weight.
It is used in a number of industrial applications such as oil well drilling, paper, explosives, mining etc., Highly refined guar gum is used as a stiffener in foods like ice cream, a stabilizer for cheeses, instant puddings and whipped cream substitutes.
Churi and Korma are bi-products contain 35% of protein and can be used as feed.
Climate and Cultivation
Guar is suitable for arid and semi-arid climates. Although guar is widely cultivated for vegetable purpose all over the country, its cultivation for seed purpose is restricted to a few northern states in kharif season. It is grown as a rainfed crop and is generally sown after the monsoon rainfall in the second half of July as it requires water before sowing.
Guar tolerates high temperatures and dry conditions It responds to irrigation but can be grown without irrigation in areas with 20cm to 50cm of annual rainfall. Crop duration varies from 90 days to 120 days depending on the varieties.
Seasons and crop calendar: Sowings are normally completed in July and plants reach flowering stage in August. However, long duration varieties take slightly longer period. Harvesting commences in the month of October in case of short duration varieties while it extends to November in case of indeterminate varieties.
 World Scenario
World production of guar seed has traditionally been confined to specific areas in India and Pakistan. Together they account for about 95% of total world production of guar seed as well as exports of guar gum. Apart from India and Pakistan, guar is also produced in smaller quantities in the U.S., Australia and African countries.
 Domestic Scenario
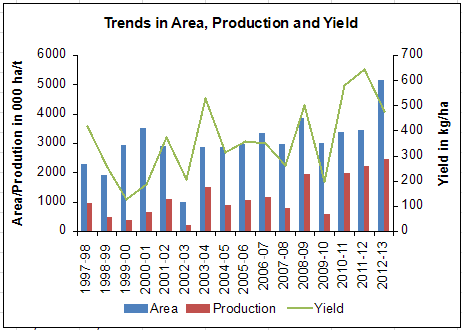
India is the single largest producer of Guar Seed accounting for 80% of the total guar produced in the world followed by Pakistan and the U.S. Although production levels of guar have been increasing steadily, output remained highly volatile owing to the crop’s dependence on climate and rainfall conditions. Area under cultivation of guar seed has crossed 30 lakh hectares in the early 2000s and has remained in the range of 30-35 lakh hectares over a decade.
 State-Wise Production
Rajasthan is the single largest state producer and has been the traditional home for guar production and trade. But the production has been highly erratic despite the relatively stable and substantial acreage under the crop due to highly fluctuating yields.
Majority of the crop is grown under rainfed conditions and hence, the yields are heavily dependent on rainfall. Nevertheless, Rajasthan alone contribute for more than 70% of India’s total output and Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab and Uttar Pradesh contribute for the rest.
 However, production pattern among other states has been changing in the recent years with a steadily raising contribution from Haryana and Punjab. Further, guar in these two states is cultivated under irrigated conditions as a result the yields are stable and very high at about 1100-1300 kg per hectare against 300-500 kg per hectare in Rajasthan.
Major Markets
Spot markets:
Rajasthan: Jodhpur, Bikaner, Sriganga nagar
Haryana: Hissar, Adampur, Bhattu, Sarsa
Gujarat: Deesa, Radhanpur
Futures markets
Futures trading in guar seed and guar gum are offered on national multi commodity exchanges including MCX, NCDEX, NMCE and ACE.
External Trade
India is the single largest exporter of guar gum in the world. India exports nearly 80-90% of the domestically produced guar gum. On average guar gum exports from India stood at about 1 to 2 lakh tonnes in 2000s.
However, there was a significant rise in exports during the past four years as they doubled from about 2.2 lakh tonnes in 2009-10 to 4.4 lakh tonnes in 2010-11 and subsequently to 7.1 lakh tonnes in 2011-12 though moderated to 4.1 lakh tonnes in 2012-13.
 Export destinations: US, China, Germany, Italy, Malaysia, Russia, Turkey, Indonesia and Egypt.
Import sources: NA
Factors Influencing Prices:
· Monsoons and rainfall: Guar seed is grown in a rainfed condition and hence fluctuations in rainfall affect supply and thereby prices
· Demand from both domestic and external sources impact prices.
· Policies: Any change in government policiesrelated to production and trade
|
Copyright © CC Commodity Info Services LLP. All rights reserved.

